Harvest season is crucial for farmers all over the world, and combines are undoubtedly at the heart of efficient farming operations, with these machines dramatically improving harvesting efficiency, minimizing losses and maintaining grain quality; however, like any complex piece of machinery, combines often face the common problems of clogging, loose belts, or loss of grain, which undoubtedly puts a damper on a farmer’s ability to produce a successful harvest.
Harvester clogging, was shut down in reverse running state, endoscopic cleanup threshing room, control feeding ≤ 80%; belt check groove wear synchronized with new, press down 4-6mm calibration tension; hydraulic system check oil level, measurement of the pump pressure, thermal imaging scanning 15 ℃ temperature difference to locate the leakage; blades to adjust the gap of 2-3mm, choose titanium plating material and according to the wheat 800-1000 hectares / rice 500-700 hectares replacement.
Understanding and solving these common problems yourself can significantly reduce downtime, avoid costly delays and maximize harvest efficiency. In this comprehensive, illustrated guide, we’ll explore the most common combine problems farmers encounter and provide clear step-by-step solutions.
Contents
- 1 Common Combine Harvester Issues & DIY Solutions
- 2 Essential Preventative Maintenance Practices
- 3 Troubleshooting Quick Reference Table
- 4 Safety First: Precautions During Repairs
- 5 Common problems and solutions for different types of combine harvesters
- 6 MINNUO after-sales service core advantages
- 7 Conclusion: Minimize Downtime, Maximize Yield
Common Combine Harvester Issues & DIY Solutions
1. Grain Header Clogging (Feed Throat Plugging)
One of the most common issues faced during harvesting operations is grain header clogging. This usually happens when wet or dense crop material accumulates in the header, causing jams and operational delays.
Keywords: Grain header clogging, combine blockage, feed throat plugging.
Symptoms:
The engine bogs down under load
Reduced feed speed and productivity
Visible crop buildup at the intake point
Step-by-step Solutions:
Step 1: Shut down the combine immediately and disengage power to the header.
Step 2: Inspect the header for clogged plant material.
Step 3: Carefully remove clogs using a header reversing system or manually clear the blockage.
Step 4: Restart slowly at reduced speed; ensure correct reel speed settings for crop conditions.
Step 5: Regularly adjust cutting heights and reel speeds to prevent future clogs.
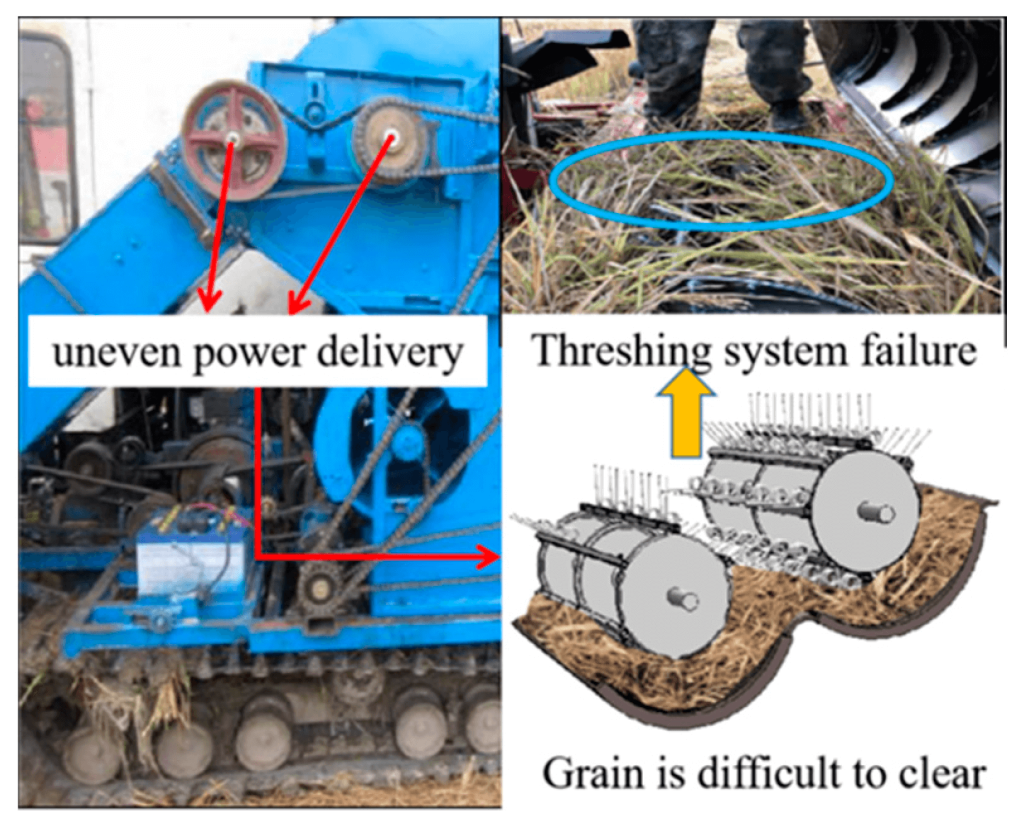
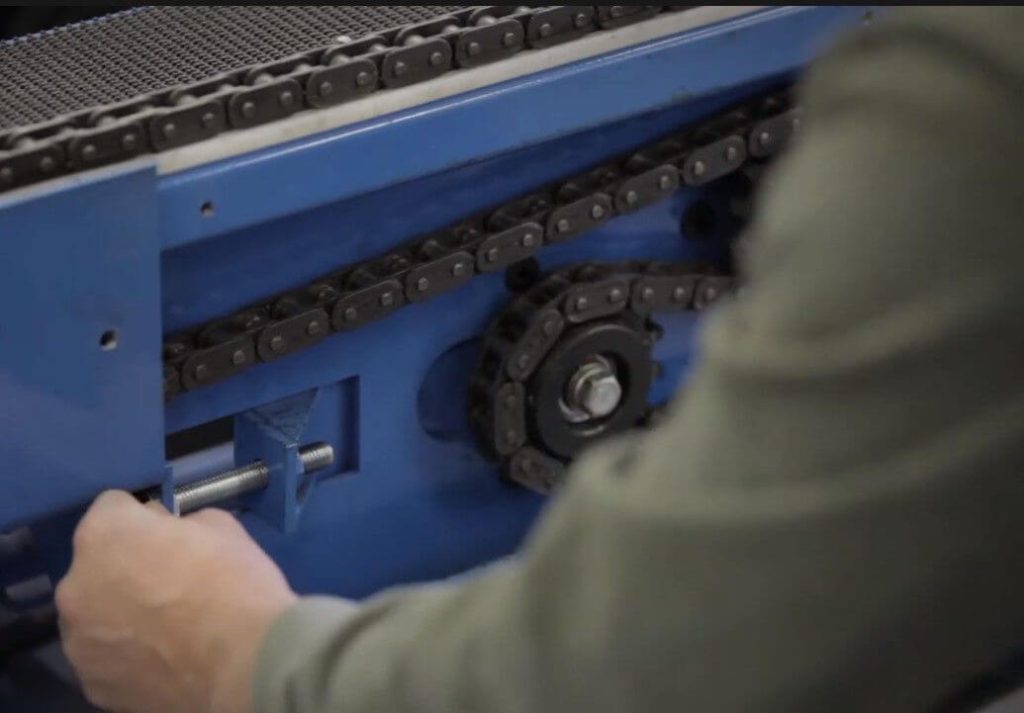
2. Conveyor and Feeder Chain Issues
The conveyor system transfers harvested material into the threshing cylinder. Problems here are common, especially when harvesting wet or tough crops.
Keywords: Feeder chain malfunction, conveyor chain adjustments, combine conveyor issues.
Symptoms:
Irregular crop feeding
Audible rattling or slipping noises
Visible slack or wear on chains
Solutions:
Step 1: Inspect the conveyor chain tension frequently (every 50 operating hours).
Step 2: Adjust chain tension using the tensioner provided by manufacturer specifications.
Step 3: Check regularly for damaged or missing chain links and replace promptly.
Step 4: Lubricate the chain with high-quality lubricants to minimize friction and extend life.

3. Threshing Drum Blockages
Keywords: Threshing drum blockage, drum speed settings, combine threshing problems.
Symptoms:
Increased engine load
Decreased grain output
Excessive noise and vibration from the drum area
Solutions:
Step 1: Immediately disengage the threshing mechanism.
Step 2: Open inspection doors and carefully remove any blockage manually (use protective gloves).
Step 3: Check threshing drum speed settings. Adjust according to the crop moisture and density.
Step 4: Inspect drum bars regularly for wear; replace if necessary.
Step 5: After clearing, gradually re-engage threshing system at a reduced initial load.

4. Loose or Damaged Belts
Keywords: Combine belt adjustment, damaged belts replacement, belt slippage.
Symptoms:
Squeaking noise under load
Belts visibly loose or cracked
Frequent slipping and reduced combine efficiency
Solutions:
Step 1: Regularly inspect belts for wear or damage at scheduled maintenance intervals.
Step 2: Adjust belt tension according to manufacturer specifications; usually performed by tightening idler pulleys.
Step 3: Immediately replace cracked, frayed, or worn belts to avoid breakdowns during critical harvest periods.
Step 4: Ensure pulleys are aligned properly to reduce uneven belt wear.
5. Excessive Grain Losses
Grain loss can significantly reduce profitability. It is crucial to monitor and mitigate losses regularly.
Keywords: Grain loss prevention, combine sieve adjustment, harvesting efficiency.
Symptoms:
Excessive grain left behind on the field after harvesting
Uneven grain distribution in storage tank
Grain blown out by cleaning fans
Solutions:
Step 1: Regularly check and adjust cleaning fan speed to match the harvested crop type and conditions.
Step 2: Adjust sieve settings carefully to optimize grain retention.
Step 3: Conduct field tests regularly; evaluate grain left behind by adjusting combine speed and settings accordingly.
Step 4: Properly set the header and reel speed; incorrect settings commonly cause excessive grain loss.

Essential Preventative Maintenance Practices
Maintaining your combine harvester in optimal condition is vital to prevent frequent breakdowns. Here’s a quick checklist to implement throughout the harvesting season:
Regularly inspect all belts and chains for tension and wear.
Perform daily lubrication of bearings and pivot points as per manufacturer’s guidelines.
Clean combine thoroughly after each harvesting day to prevent build-up of crop residue.
Perform periodic inspections and timely replace worn parts to ensure peak efficiency.

Troubleshooting Quick Reference Table
| Problem Area | Common Issues | Quick Solution |
| Header | Clogging | Manual Clearing, Adjust reel speed |
| Conveyor | Loose chains | Adjust tensioner, lubrication |
| Threshing | Drum blockage | Manual clearing, adjust drum speed |
| Belts | Slippage | Tighten/replace belts, align pulleys |
| Grain Loss | Sieve setting | Adjust sieve and fan speed |
Safety First: Precautions During Repairs
Always follow safety guidelines when performing any maintenance or repairs:
Turn off the combine engine before attempting maintenance or inspection.
Wear personal protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear.
Use manufacturer-approved tools and parts.
Work on a stable and level surface to avoid injury.
Common problems and solutions for different types of combine harvesters
I. Full-feeding combine harvesters (e.g. Lavo Gushen series, Zoomlion 4LZ series)
1. Cutting platform blockage
Problem: Crops are piled up at the entrance of the cutting deck, resulting in failure to convey properly.
Cause: The speed of the paddle wheel does not match the forward speed, and the gap between the auger blade and the bottom plate is too large.
Solution:
Adjust the speed of the paddle wheel to 1.1-1.2 times higher than the forward speed.
Reduce the clearance between the spiral blade and the bottom plate to 10mm (low crop) or repair the worn blade.
2. Drum clogging
Problem: Threshing drum is jammed due to weeds or wet crops.
Cause: too small drum clearance, excessive engine load or high crop moisture.
Solution:
Increase the clearance between the drum and the concave plate (wet crops need additional adjustment).
Reduce the operating speed or pause the operation to clear the blockage.
3. Threshing is not clean
Problem: The threshed material contains unthreshed ears.
Reason: Insufficient drum speed, wear and tear of concave plate or excessive feeding.
Solution:
Increase drum speed or replace worn ribs/concave plates.
Reduce the feeding volume and keep the large throttle operation.
Ⅱ.Semi-fed combine harvester (such as Kubota PRO series, Yanmar YH series)
1. Clip feed chain slippage
Problem: The chain is unable to convey the stalks effectively.
Cause: Chain slack, sprocket wrapped with grass or friction plate worn.
Solution:
Tension the chain until the middle section sags 15mm.
Clean up the weeds in the sprocket or replace the worn friction plate.
2. Threshing mouth does not produce grain
Problem: The threshing drum is blocked by weeds, resulting in no seed output.
Reason: too much debris in the drum or insufficient engine power.
Solution:
Stop the machine to clean the drum and adjust the gap.
Check the engine belt tension.
3. High leakage rate
Problem: Unharvested crop left in the field.
CAUSE: Blunt cutter, improper cutting height or blind area not covered.
Solution:
Replace sharp blades and calibrate cutting range.
Adjust the cutting height according to the direction of fall.
Ⅲ.Corn special harvester (such as Dima 4YZ series, Bold 4YL series)
1. Cob picking roller blockage
Problem: Corn ears are stuck and cannot enter the conveyor system.
Reason: Excessive knife clearance or slackness in the clamping chain.
Solution:
Reduce the knife gap and tighten the pinch chain.
Clean up the picking roller tangles.
2. peeling machine efficiency is low
Problem: Bract residue or peeling roller stalled.
Reason: The position of the pressure feeder is too high or the rubber plate is aging.
Solution:
Adjust the height of the pressure feeder to a suitable position.
Replace the aging rubber plate and clean the debris between the rollers.
3. Shredder winding
Problem: The blade is entangled by the straw causing the rotor to stop.
Reason: The height of the blade is too low or the belt is slipping.
Solution:
Adjust the distance between the blade and the ground to more than 30mm.
Tension the belt or replace the worn blades.
MINNUO after-sales service core advantages
① Intelligent monitoring cloud platform
Real-time monitoring: through the vehicle-mounted MN-Box terminal, 32 parameters such as speed, temperature, vibration, etc. are uploaded every 10 seconds;
Early Warning Push: Predict failures 48 hours in advance (e.g. bearing wear >80% automatically sends labor);
Case: a user received an alert of “abnormal transmission oil temperature”, and the engineer remotely guided the replacement of the filter element, avoiding a 50,000 RMB level overhaul.
② Spare parts warranty replacement policy
Warranty scope: powertrain (3 years/3000 hours), hydraulic system (2 years/2000 hours), electrical components (1 year unlimited);
Replacement process: submission of fault code → customer service confirmation → delivery to the nearest warehouse (85% of commonly used parts 24 hours to reach);
Specialty services: old parts discount recycling (up to 30% of the cost of new parts), reduce maintenance costs.
③ UNPROFOR network
Provide 7×24 hours on-site support during busy season (including 50% expediting fee subsidy at night);
Support third-party brand equipment maintenance (10%-15% service charge).
Frequently Asked Questions Quick Response Table
| Question Type | MINNUO Commitment Time Limit | Support Mode |
| Consultation | Response within 5 minutes | 400 hotline/online customer service |
| General faults | 12 hours door-to-door | Local service provider with spare parts |
| Major faults | 48 hours to repair | Headquarter engineers + air transportation of spare parts |
| Extended Warranty Claims | Reviewed within 3 working days | Claims are automatically processed by uploading vouchers on APP. |
Conclusion: Minimize Downtime, Maximize Yield
Understanding common combine problems and knowing how to troubleshoot them can save a lot of time and money during the busy harvesting period, and regular self-inspections, timely maintenance and proper adjustments can significantly extend the life of your combine and improve operational efficiency.
MINNUO has 36 years of experience in harvester manufacturing and maintenance, want more expert tips on how to efficiently run your farm operations and maintain your machinery? Subscribe to our newsletter or contact our agricultural machinery experts today!
A proactive approach not only prevents downtime, but also ensures that you maximize your gains with minimal losses.
We wish you a happy harvest!

